Database-First approach in Entity Framework Core

In Database-First approach the entity and context classes are automatically created by the EF Core from the database. So this means you have to first create your database for the app.
Let me show you how to do this for a Company’s Database.
Creating Database in SQL Server
Open the View ➤ SQL Sever Object Explorer in Visual Studio. Then create a simple company’s database in your SQL Server and name it Company. Create 2 tables to it and name them as:
- 1. Employee
- 2. Department
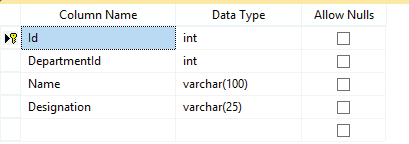
The id column is both Primary Key and Identity.
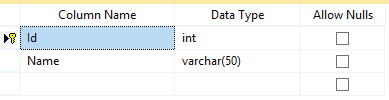
The id column is both Primary Key and Identity.
There is One-to-Many relationship between the Employee & Department table. This means one department can have multiple employees.
Here we have created the DepartmentId column of Employee table as the foreign key for the Id column of the Department table.
We can create these 2 tables by running the create table scripts on the New Query Window. Right click on the Company database and select “New Query”. A window will open where we need to enter the given scripts and click the “Execute” button.
Department table
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Department](
[Id] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[Name] [varchar](50) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Department] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[Id] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]Employee table
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Employee](
[Id] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[DepartmentId] [int] NOT NULL,
[Name] [varchar](100) NOT NULL,
[Designation] [varchar](25) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_Employee] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[Id] ASC
)WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY]
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
SET ANSI_PADDING OFF
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[Employee] WITH CHECK ADD CONSTRAINT [FK_Employee_Department] FOREIGN KEY([DepartmentId])
REFERENCES [dbo].[Department] ([Id])
GO
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[Employee] CHECK CONSTRAINT [FK_Employee_Department]
GOEntity Framework Core Database Connection String
A database connection string contains information about a data source which is a database engine, as well as the information necessary to connect to it. Entity Framework Core needs connection string to communicate with the database and perform database operations like creating records, reading records and so on. We can easily find the Database Connection String by opening the SQL Sever Object Explorer then right click on the database to open the “Properties” options. Select it.
In the properties window find the Connection String field and simply copy it’s value from there. We have shown this in the below video.
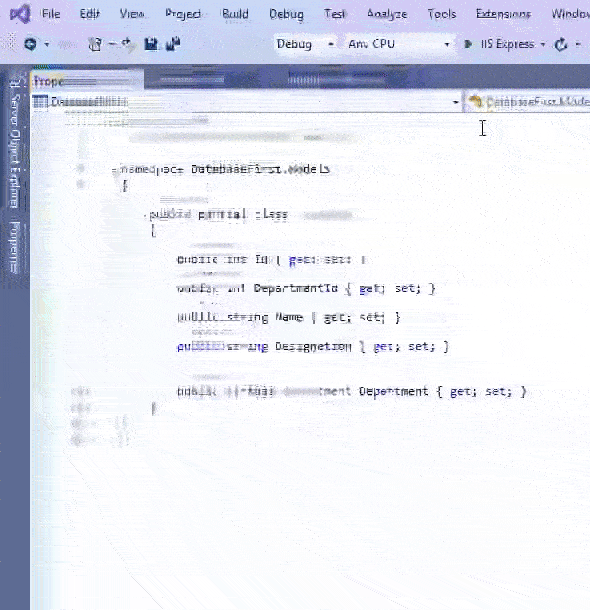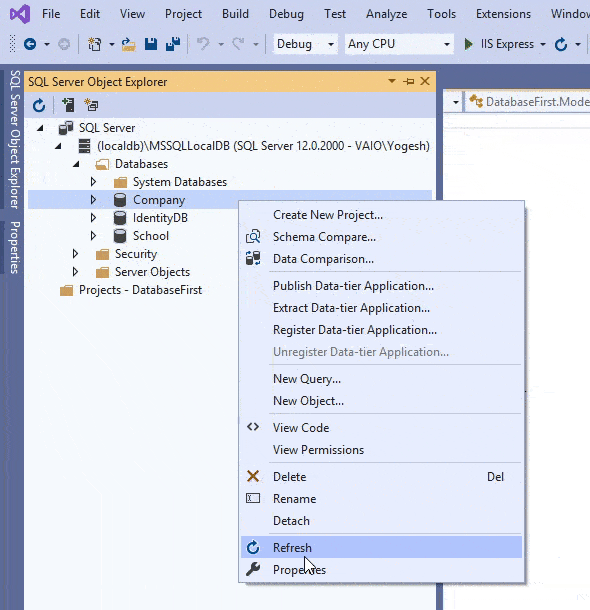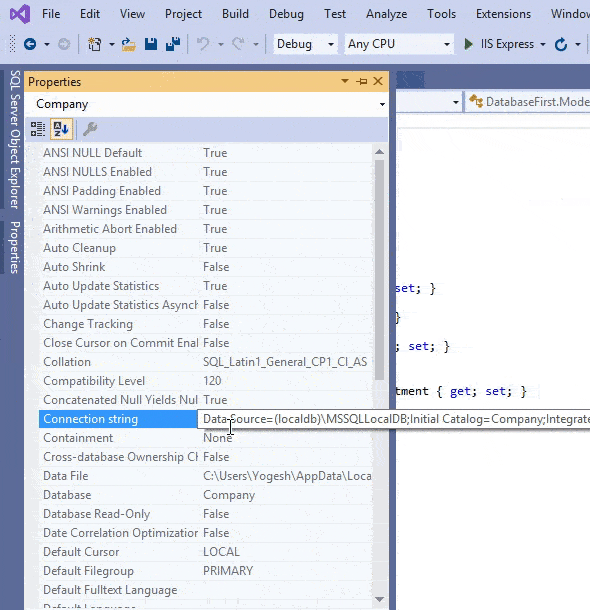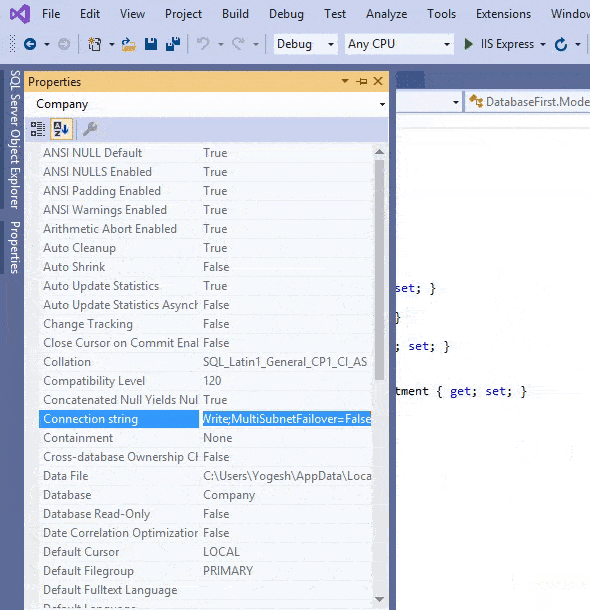
The Database Connection String in our case is:
Server=vaio;Database=Company;Trusted_Connection=True;The connection string has following informations:
- The Database server name is given as Server=vaio.
- Database=Company is the name of the database.
- Trusted_Connection=True specifies the Windows authentication i.e. it will use Windows credentials to connect to the SQL Server. On live servers we use SQL Server Authentication which has an SQL Server user name and password.
.NET Core command-line interface (CLI) Scaffold Command
Now we run the CLI Scaffold Command on the Package Manager Console window. Open this window from Tools ➤ NuGet Package Manager ➤ Package Manager Console menu in Visual Studio.
The command to run is shown below. Make sure to run this command from the directory of your project file.
PM> dotnet ef dbcontext scaffold "Server=vaio;Database=Company;Trusted_Connection=True;" Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -o ModelsNote the following things:
- Inside the quotation marks (“”) is the Database Connection String which is Server=vaio;Database=Company;Trusted_Connection=True;. It may be different on your case.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer; is the name of the provider for SQL Server.
- -o Models refers to the directory name where all the classes will be generated. Here it is the Models folder.
The command will take nearly 10 to 20 seconds to execute and it will generate the context & entity model classes inside the Models folder.
Context & Entity Classes
We will find the context & entity classes generated by DOT NET inside the Models folder.
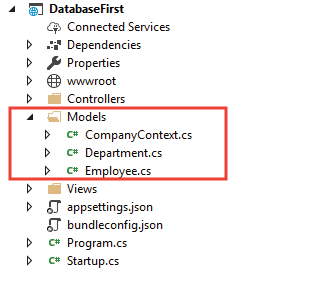
The 2 entity Classes created are the Employee.cs & Department.cs.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace DatabaseFirst.Models;
public partial class Employee
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public int DepartmentId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; } = null!;
public string Designation { get; set; } = null!;
public virtual Department Department { get; set; } = null!;
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace DatabaseFirst.Models;
public partial class Department
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; } = null!;
public virtual ICollection<Employee> Employees { get; set; } = new List<Employee>();
}
The database context class created is CompanyContext.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace DatabaseFirst.Models;
public partial class CompanyContext : DbContext
{
public CompanyContext()
{
}
public CompanyContext(DbContextOptions<CompanyContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
public virtual DbSet<Department> Departments { get; set; }
public virtual DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
=> optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Data Source=(localdb)\\MSSQLLocalDB;Initial Catalog=Company;Integrated Security=True;Connect Timeout=30;Encrypt=False;Trust Server Certificate=False;Application Intent=ReadWrite;Multi Subnet Failover=False");
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Department>(entity =>
{
entity.ToTable("Department");
entity.Property(e => e.Name)
.HasMaxLength(50)
.IsUnicode(false);
});
modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>(entity =>
{
entity.ToTable("Employee");
entity.Property(e => e.Designation)
.HasMaxLength(25)
.IsUnicode(false);
entity.Property(e => e.Name)
.HasMaxLength(100)
.IsUnicode(false);
entity.HasOne(d => d.Department).WithMany(p => p.Employees)
.HasForeignKey(d => d.DepartmentId)
.OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.ClientSetNull)
.HasConstraintName("FK_Employee_Department");
});
OnModelCreatingPartial(modelBuilder);
}
partial void OnModelCreatingPartial(ModelBuilder modelBuilder);
}
Package Manager Console (PMC) Scaffold-DbContext Command
We can skip the DotNet CLI Scaffold Command and use Scaffold-DbContext Command for creating context & entity classes from a database. This will do the exact same thing like before.
Run the following command on the Package Manager Console.
PM> Scaffold-DbContext "Server=vaio;Database=Company;Trusted_Connection=True;" Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir ModelsDownload the source codes:
We just finished understanding Entity Framework Core Database First approach and created the necessary model and database context from the sql server database by running the Scaffold commands. However just keep this in mind that Database First approach is not used anymore instead we will be using Code-First Approach as Microsoft itself put emphasis on using this approach.
Before that we need to understand how Database Context will work. This is the tutorial coming next – DbContext Class in Entity Framework Core








 Welcome to YogiHosting - A Programming Tutorial Website. It is used by millions of people around the world to learn and explore about ASP.NET Core, Blazor, jQuery, JavaScript, Docker, Kubernetes and other topics.
Welcome to YogiHosting - A Programming Tutorial Website. It is used by millions of people around the world to learn and explore about ASP.NET Core, Blazor, jQuery, JavaScript, Docker, Kubernetes and other topics.