How to Perform CRUD Operations in SQL Server
CRUD Operations stands for Create, Read, Update and Delete, these are the basic functions of any database. In this tutorial I will teach how to perform CRUD in SQL Server.
Read = Select Records from a Table
Update = Update Records in a Table
Delete = Delete Records from a Table
Create a Student Table
I will first create a Student Table to perform CRUD Operations. This table contains the information of students in a School.
In the Object Explorer of SQL Server right click on the Databases node and select New Database.
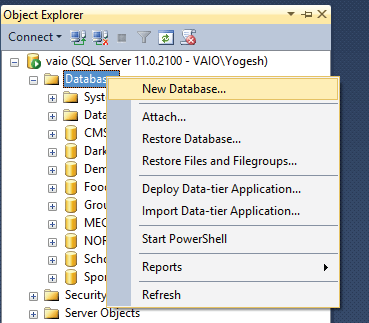
On the new window that opens, give the Database name and press the OK button.
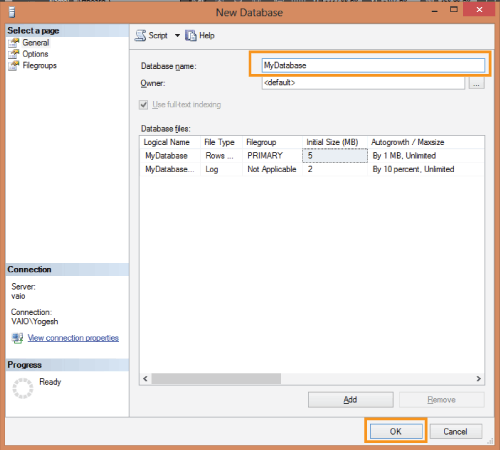
This will create your database.
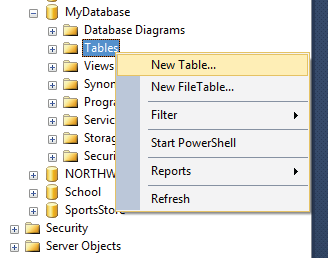
Next make Student table in this newly created database.
Right click on the Tables node of the database and select New Table.
| Column Name | Data Type | Allow Nulls | Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
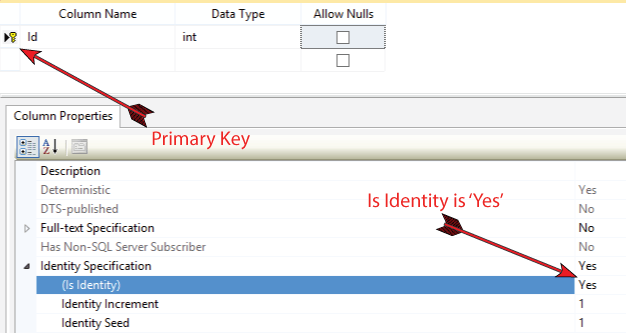
| Id | Int | No | Primary, Identity |
| Name | Varchar(50) | No | – |
| Address | Varchar(100) | Yes | – |
| Age | Int | No | – |
| Standard | Varchar(10) | No | – |
| [Percent] | Decimal(5,2) | No | – |
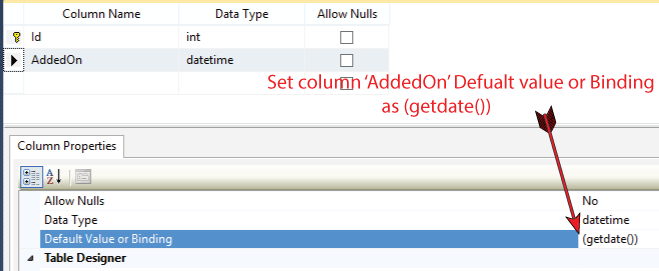
| AddedOn | Datetime | No | Default Value or Binding = getdate() |
| Status | Bit | No | – |
For the column AddedOn, set its Default Value or Binding as (getdate()).
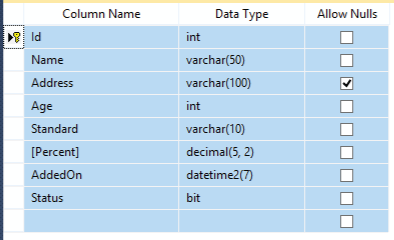
This is how the Student table looks like:
Create Table Query
The syntax of Create table Query in SQL Server is:
CREATE TABLE TableName
(
column_name1 data_type,
column_name2 data_type,
column_name3 data_type,
....
)
You can also create the Student table by the below Create Table Query:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Student]
(
Id int IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
Name varchar(50) NOT NULL,
Address varchar(100) NULL,
Age int NOT NULL,
Standard varchar(10) NOT NULL,
[Percent] decimal(5, 2) NOT NULL,
AddedOn datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT GETDATE(),
Status bit NOT NULL
)
Insert Data into a Table
To insert data in the Student table I will use SQL Server Insert Statement. The syntax of the Insert Statement is:
INSERT INTO TableName (column1,column2,column3,...)
VALUES (value1,value2,value3,...)
Using the below Insert statement, I can Insert the Records in the Student table:
Insert Into Student(Name,Address,Age,Standard,[Percent],Status)
Values('James Martin','25 Bedford St. New York City, N.Y. 10014',13,9,72.32,1)
After running the insert query the table will show the inserted record.

I can also create a Stored Procedure which will insert a record in the Student table when executed. The Insert Stored Procedure is:
CREATE PROCEDURE SP_InsertStudent
@Name VARCHAR(50),
@Address VARCHAR(100),
@Age INT,
@Standard VARCHAR(10),
@Percent DECIMAL(5, 2),
@Status BIT
AS
BEGIN
Insert into Student(Name,Address,Age,Standard,[Percent],Status) Values(@Name,@Address,@Age,@Standard,@Percent,@Status)
END
To execute this stored procedure use the below statement:
EXEC [dbo].[SP_InsertStudent]
@Name = 'James Martin',
@Address = '25 Bedford St. New York City, N.Y. 10014',
@Age = 13,
@Standard = '9',
@Percent = 72.32,
@Status = 1
Select Statement to Read the Records
To read records from a table use Select Statement. To get all records from Student table use:
Select * From StudentThe Stored procedure that returns all Students based on age which is given in the Parameter:
CREATE PROCEDURE SP_SelectStudent
@Age INT
AS
BEGIN
Select * FROM Student Where Age=@Age
END
In the above Stored Procedure you have to provide the value for the @Age parameter. The Stored Procedure will then returns all the students that have the Age same as @Age value.
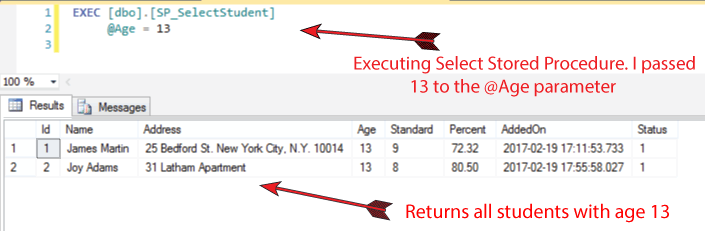
Look at the below Statement which executes the Select Procedure. I passed the value 13 to @Age parameter and therefore it will return all students who are 13 years old.
EXEC [dbo].[SP_SelectStudent]
@Age = 13
Update Statement to Update Records
To update one or more records in a table use Update Statement whose syntax is:
Update TableName SET column1=value1,column2=value2
In the Student table, to Update the standard of the student with Id 2, the SQL Query becomes:
Update Student Set Standard=9 Where Id=2
I can create a Stored Procedure that will perform the Update on name,address, age, standard, percent and status for a student that has an id given by @Id parameter.
All the values are passed to the parameters of the Stored Procedure.
CREATE PROCEDURE SP_UpdateStudent
@Id INT,
@Name VARCHAR(50),
@Address VARCHAR(100),
@Age INT,
@Standard VARCHAR(10),
@Percent DECIMAL(5, 2),
@Status BIT
AS
BEGIN
Update Student Set Name=@Name,Address=@Address,Age=@Age,Standard=@Standard,[Percent]=@Percent,Status=@Status WHERE Id=@Id
END
Let us execute the above stored procedure to update the student with id ‘2’.
EXEC @return_value = [dbo].[SP_UpdateStudent]
@Id = 2,
@Name = 'Jack Clinton',
@Address = '12 Block, House no 2',
@Age = 14,
@Standard = '10',
@Percent = 73.88,
@Status = 0
The above execute statement changes the name, address, age, standard, percent and status of that student.
The below images show the updated record for the student with id 2:
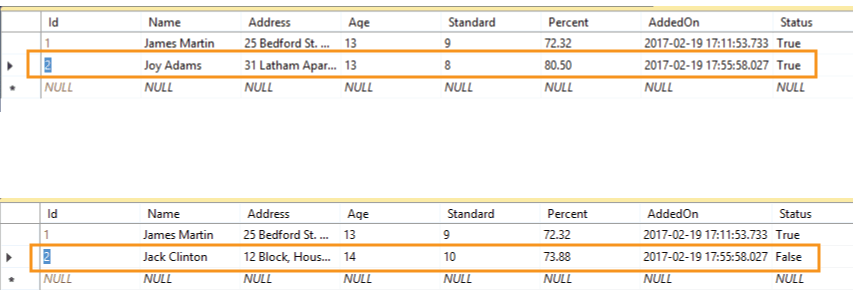
Delete Statement to Delete Records
Through the Delete Statement one or more records can be deleted from the table. It’s syntax is:
Delete From TableName
Use Where Clause with Delete Statement when you want to delete certain records.
The below Query deletes all the students that aged less than 10.
Delete From Student Where Age <10
I can also create a Stored Procedure that deletes all the students that are less than a specific age.
This specific age is sent to the parameter of the stored procedure.
CREATE PROCEDURE SP_DeleteStudent
@Age INT
AS
BEGIN
Delete Student WHERE Age< @Age
END
To delete all the student that aged less than 5 year the query becomes:
EXEC SP_DeleteStudent
@Age = 5
Hope you enjoyed learning the CRUD Operations in SQL Server. Let me know if you have any questions.








 Welcome to YogiHosting - A Programming Tutorial Website. It is used by millions of people around the world to learn and explore about ASP.NET Core, Blazor, jQuery, JavaScript, Docker, Kubernetes and other topics.
Welcome to YogiHosting - A Programming Tutorial Website. It is used by millions of people around the world to learn and explore about ASP.NET Core, Blazor, jQuery, JavaScript, Docker, Kubernetes and other topics.